Home » Achievements (Page 2)
Category Archives: Achievements
Recent Posts
- Strengthening Industry Collaboration: CSE Hosts IAB Meeting for CS and CE Programs
- CSE Students Secure First Place at Snoonu Hackathon 2026
- CSE Faculties Receive Grants on Institutional Collaboration between Qatar University & Khalifa University
- Computer Engineering Practicum Demo Day & Contest (4th Edition)
- CSE faculty receives research funding from Google
Archives
- January 2026
- December 2025
- November 2025
- September 2025
- August 2025
- May 2025
- February 2025
- January 2025
- December 2024
- November 2024
- September 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
Categories
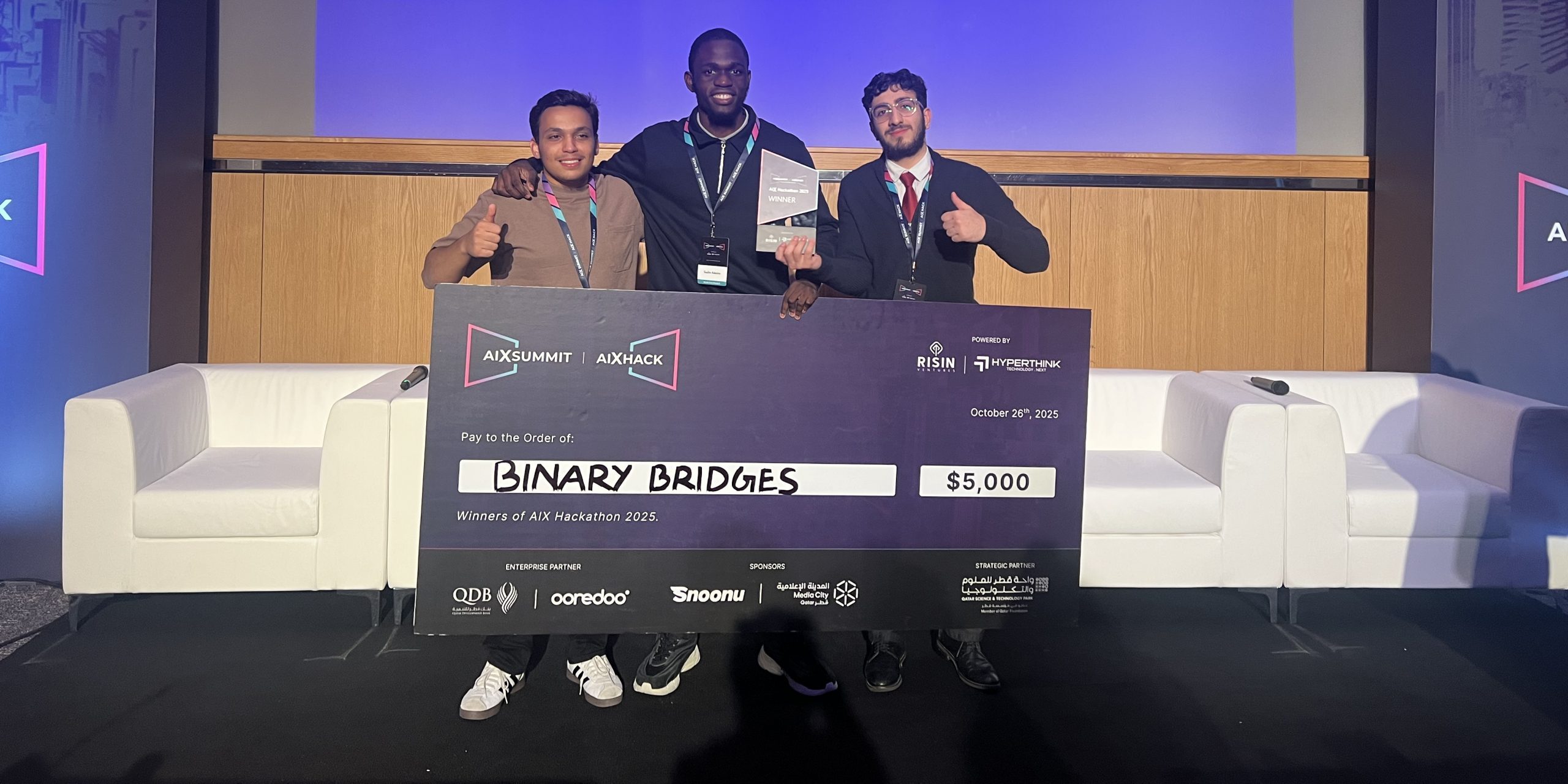
QU Students Win First Place at the AIX Summit Hackathon!
November 12, 2025 / Leave a comment
A talented team of Qatar University students, including two from our CSE department, has proudly won first place at the AIX Summit Hackathon, organized by Risin Ventures and sponsored by Ooredoo and Qatar Development Bank (QDB). The event was held at the Qatar Science & Technology Park (QSTP) and brought together top innovators to develop AI-driven solutions to real-world challenges.
The winning team, including Ahmed Khedr Elsheshtawy (First-Year Computer Science), Saalim Adesina (First-Year Computer Science), and Zaid Abubaker Al Samarie (Second-Year Medicine), developed an AI-powered application that automates the generation of due diligence reports for startups. The tool assesses the investment potential of emerging businesses by integrating modern web frameworks such as React and leveraging large language models (LLMs) like Google Gemini to analyze key financial and operational data.
This innovation aims to make investment analysis faster and more reliable, supporting investors and analysts in making data-driven decisions.
Congratulations to the team for representing Qatar University with excellence and innovation!
CSE Faculty Secures QRDI Grant Award for AI-Integrated Islamically-Grounded Psychotherapy
September 28, 2025 / Leave a comment
Prof. Junaid Qadir, a faculty member of our CSE department, and his interdisciplinary team have secured a $300,000 research grant over 24 months from the Qatar Research, Development, and Innovation Council (QRDI). Awarded under the “Advancing Neuro and Mental Health Research” (ANMR) Call, this project highlights the team’s pioneering leadership at the intersection of technology, faith, and mental health.

The funded initiative, titled “Integrating Generative AI with Traditional Islamically Integrated Psychotherapy (TIIP) for Religious OCD”, brings together experts from across institutions and disciplines. The project is led by Prof. Qadir (Qatar University) alongside Dr. Hooman Keshavarzi (Hamad Bin Khalifa University), Dr. Alaa Ali Abd-Alrazaq (Weill Cornell Medicine—Qatar), and Dr. Syed Ibrahim Ghaznavi (Information Technology University, Pakistan).
The research addresses scrupulosity, a form of religious obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). This condition manifests in intrusive doubts, compulsive rituals such as repeated purification or obsessive prayer, and deep feelings of guilt over perceived sins. To respond to this challenge, the project will design a mobile and web platform anchored by a Generative AI–powered chatbot. The chatbot, carefully fine-tuned under the supervision of TIIP experts, will deliver timely, Islamically-authentic therapeutic support while maintaining strict privacy and ethical safeguards.
By blending TIIP, behavioral science, and responsible Generative AI, the project introduces a culturally grounded and scalable model for addressing religious OCD in Muslim-majority societies. Crucially, the approach keeps human connection at its core while using AI to enhance personalization, engagement, and accessibility for those in need.
This project not only sets a precedent for integrating cutting-edge AI with culturally authentic psychotherapy, but also signals a new frontier in mental health care that is both innovative and deeply rooted in tradition.
Congratulations to Prof. Junaid and his team!
CSE Dept. Honored at Huawei’s “Innovation in Education and Talent Excellence” Event
August 24, 2025 / Leave a comment
The Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE) at Qatar University was proudly honored through its faculty and community at the prestigious Huawei ICT Academy Awards. This year, Prof. Amr Mohamed was honored with the Best Leadership Award, Dr. Moutaz Saleh received the Best Instructor Award 2024, and the CSE Department was recognized with the Excellence Achievement Award 2024.



These accomplishments highlight the department’s leading role in advancing innovation, academic leadership, and talent development in Qatar.
The awards were presented during the event “Innovation in Education and Talent Excellence Award”, held on 21st August 2025 at the Huawei Exhibition Centre, UDC Tower, Pearl Island. The gathering brought together Huawei’s university partners, faculty members, professors, and industry leaders to celebrate the remarkable achievements of students and educators who are shaping Qatar’s digital future.
The event not only honored outstanding contributions but also sparked discussions on the latest innovations in education—fostering inspiration for the next generation of digital leaders. A highlight of the evening was the recognition of Qatar’s talented youth, including the ICT Skills & Innovation Competition Winners 2024–2025, who continue to set new benchmarks for creativity and technical excellence.
CSE faculties and students awarded at CENG 2025 End of Year Event
May 28, 2025 / Leave a comment
The CSE faculties and students have proudly received several awards in several competitions at the College of Engineering End of Year event that was held on May 26, 2025.
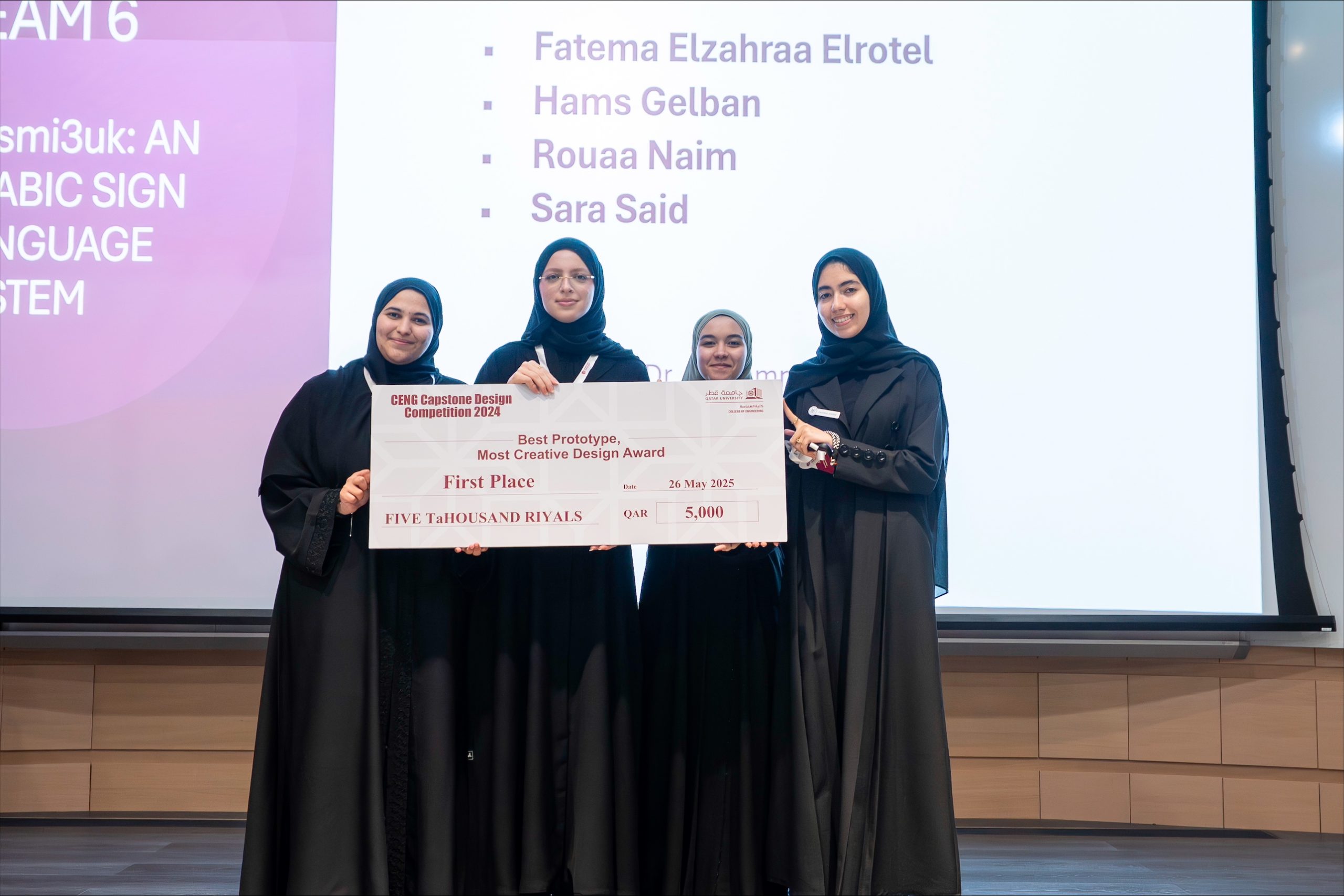
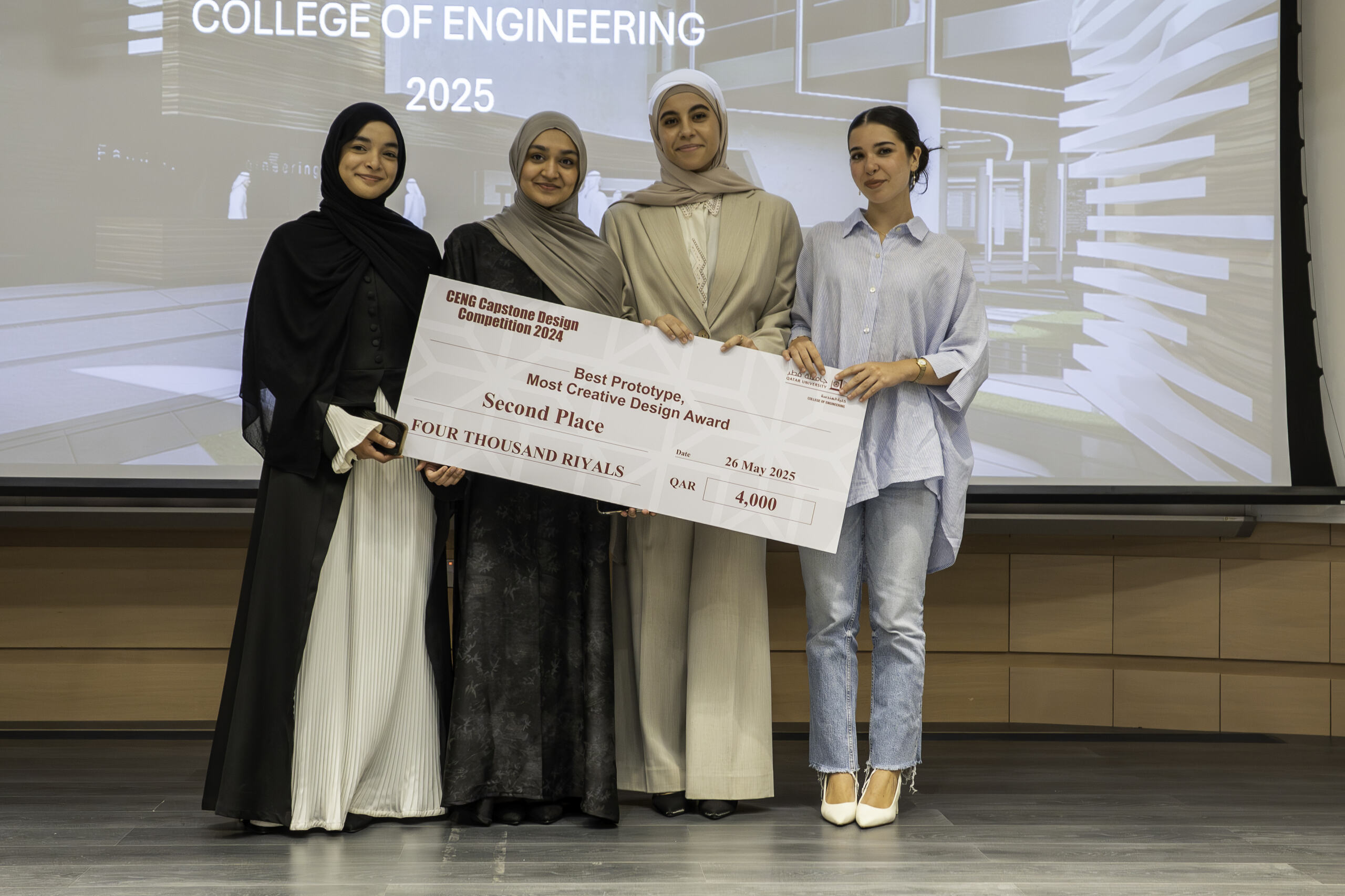
The graduation projects competition included two categories: Best Prototype Most Creative Design, and Best Marketable Design. The first place in the Best Prototype Most Creative Design category was awarded to the project titled “Nusmi3uk: An Arabic sign language system” from the Computer Science program. This project was developed by the students Fatema Elzahraa Elrotel, Hams Gelban, Rouaa Naim, and Sara Said under the supervision of Dr. Mohammad Saleh.

The second place in the same Best Prototype Most Creative Design category was awarded to the project titled “Prosthetic Arm with Neural Interface” from the Computer Engineering program. This project was developed by the students Amnath Abdeen, Sifna Nasar, Vasiliki Maria Gerokosta, and Yomna Mohamed under the supervision of Dr. Loay Ismail.
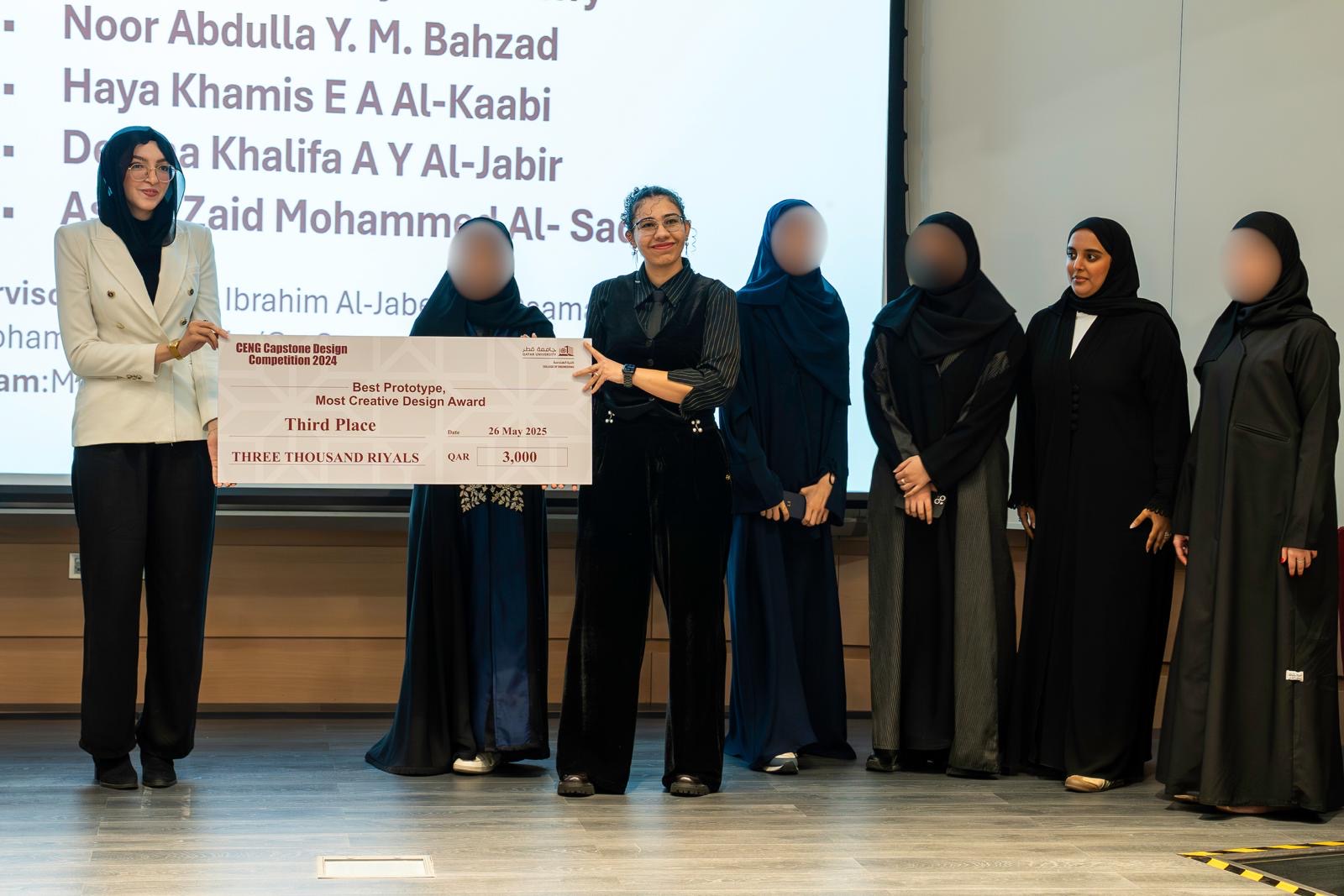
The third place in the same Best Prototype Most Creative Design category was awarded to the project titled “Transforming Hand Rehabilitation: The Development of Soft Actuators, Extended Reality (XR) Environments, and Doctor-Patient Interaction Platform” that was a multidisciplinary senior design project. This project was developed by the students Fatma Elbadrawy, Ferial Marzouk, Ekram Omar, and Lama Albanna from Computer Science Program, in addition to Noor Bahzad, Asma Al-Sadi, Haya Al-Kaabi, and Deema Al-Jabir from industrial and systems engineering. The project is supervised by Dr. Osama Halabi, Dr. Faisal Al-Jaber, and Dr. Mohammed Al-Sada.
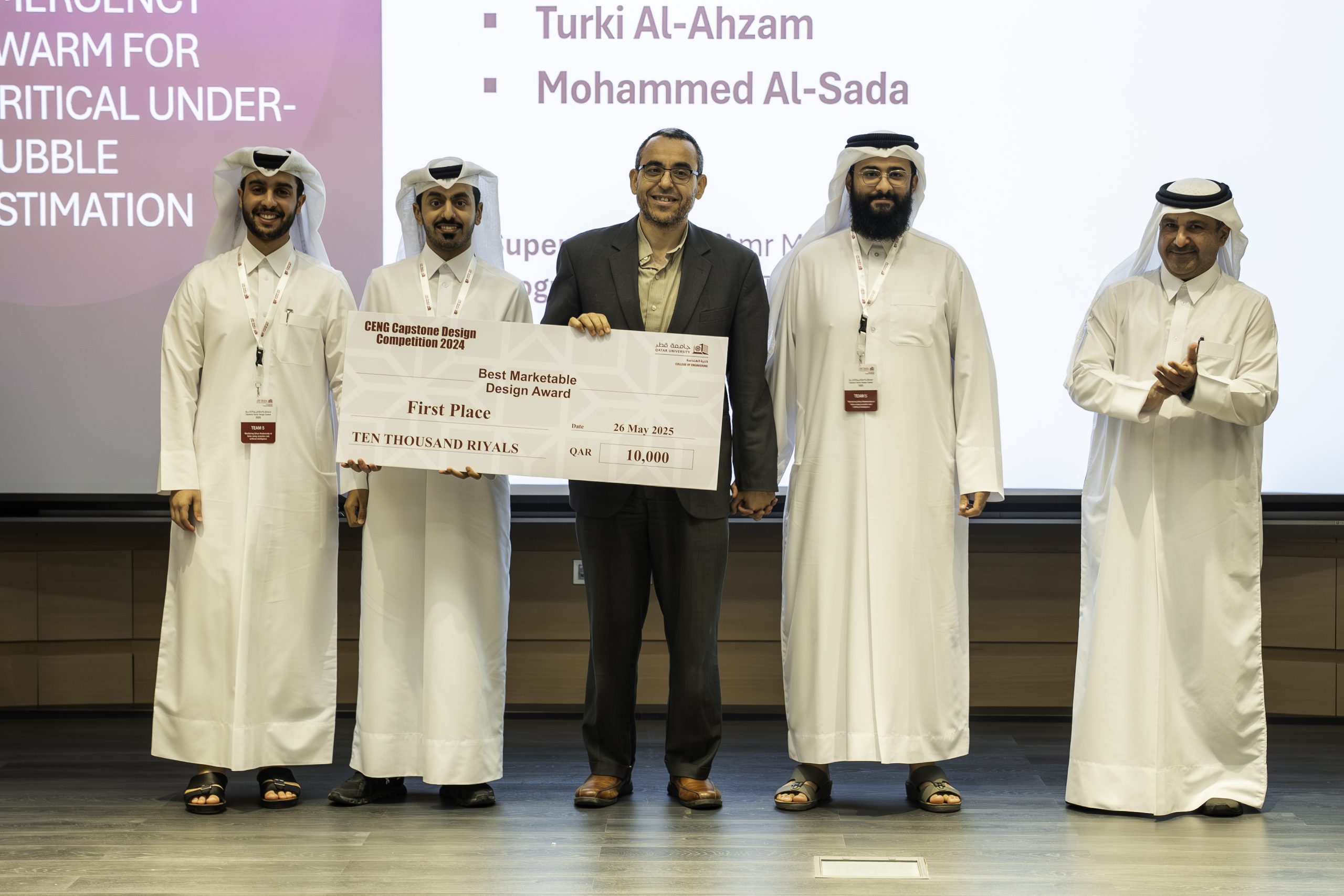
In the Best Marketable Design category, the first place was awarded to project titled “RESCUE: Radar-based Emergency Swarm for Critical Under-rubble Estimation”. The team included the students Jeham Al-Kuwari, Sultan Al-Harami, Turki Al-Ahzam, and Mohammed Al-Sada from Computer Engineering Program. The project is supervised by Prof. Amr Mohamed.

Finally, the Dean’s Award for Services for the academic year 2025 was received by Prof. Junaid Qadir for Faculty Members Category.

CSE PhD Student and Team Win First Place at ICMHI 2025 for Surgical Gesture Recognition Research
May 22, 2025 / Leave a comment
Dehlela Shabir, a PhD student at the CSE, Prof. Khaled Shaban, and Dr. Nikhil Navkar from Hamad Medical Corporation (HMC) have been awarded the first place in the student essay competition – PhD session, for their paper titled “Deep Learning-Based Gesture Recognition for Enhanced Laparoscopic Suturing Skill Evaluation and Training” at the 9th International Conference on Medical and Health Informatics (ICMHI 2025), held in Kyoto, Japan, from May 16-18, 2025.
ICMHI is an international platform for scientists, engineers, and technologists to showcase innovations in medical and health informatics, with topics ranging from biomedical data mining and medical image processing to cloud computing and personalized treatment. The paper is part of an ARG-awarded project, developed in collaboration with the Department of Surgery at HMC. The project focuses on improving skill acquisition in laparoscopic surgeries through automated gesture recognition using deep learning.
The team is working on several tasks aimed at advancing automation in surgical education and practice, including robotic minimally invasive surgery, mixed reality training, and the emerging concept of a surgical metaverse.

CSE SDP Contest Day 2025
May 15, 2025 / Leave a comment
On May 6th 2025, the highly anticipated senior project presentations took place at the state-of-the-art new engineering building H07. These remarkable projects, the culmination of tireless efforts by talented students, were subjected to rigorous evaluation by examiners from the CSE department. After careful deliberation, outstanding projects from each program, Computer Science (CS) and Computer Engineering (CE), emerged victorious. Exceptional teams of those winners will be chosen to proudly represent our department in the upcoming college contest. We eagerly anticipate the success that awaits our representatives as they compete at the college level, confident in their abilities, to make our department proud once again.
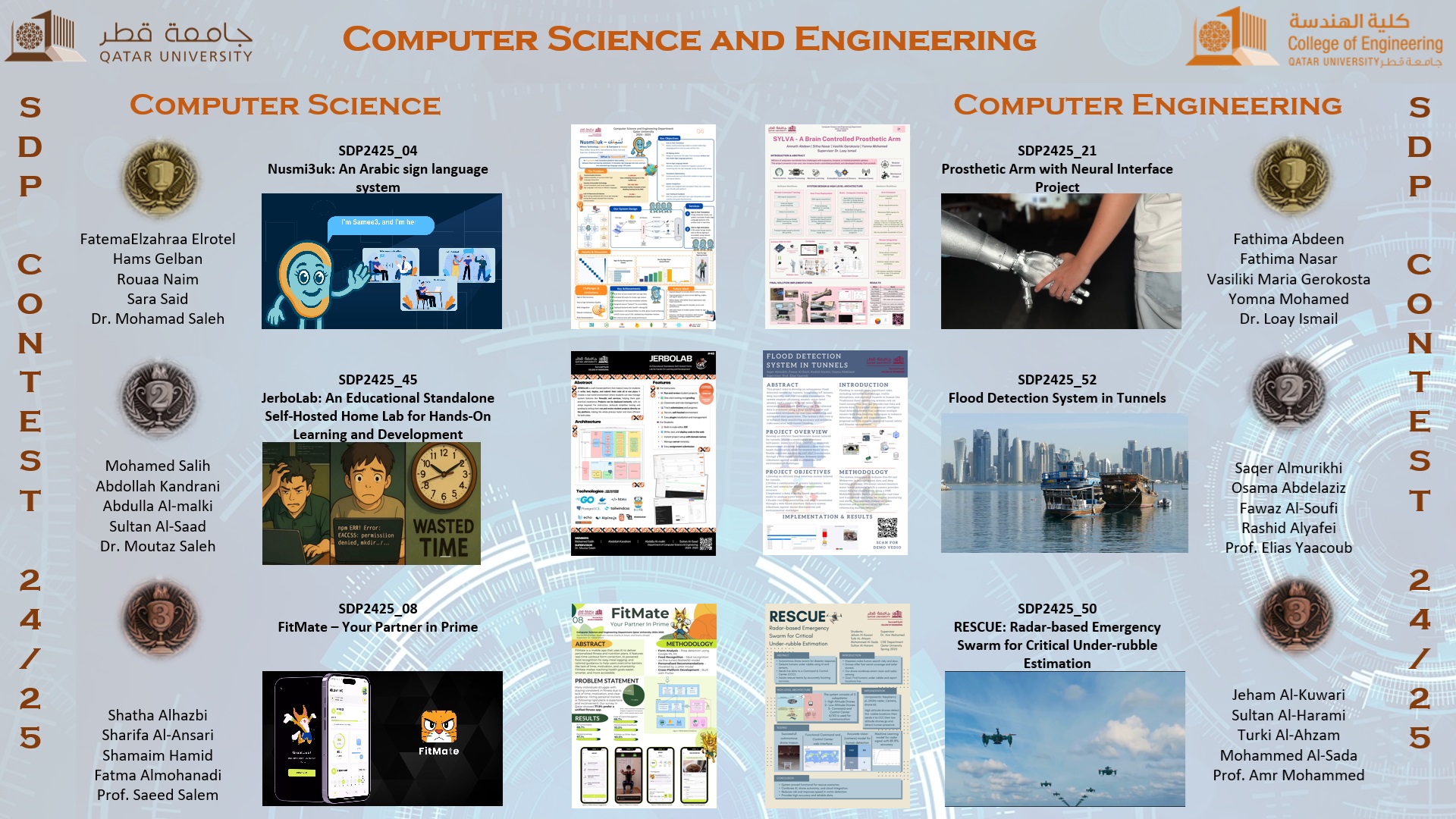
Winning Projects in CSE-SDP23 Contests Day
CE Rank 1
Project title: Prosthetic Arm with Neural Interface Project
Students: Fathima Amnath Abdeen, Fathima Sifna Nasar, Vasiliki Maria Gerokosta, and Yomna Mohamed.
Supervisor: Dr. Loay Ismail
CE Rank 2
Project title: Flood Detection System in Tunnels
Students: Saqer Almurikhi, Osama Abdelaziz, Fawaz Al-Soufi , and Rashid Alyafei
Supervisor: Prof. Elias Yaacoub.
CE Rank 3
Project title: RESCUE: Radar-based Emergency Swarm for Critical Under-rubble Estimation
Students: Jeham Al-Kuwari , Sultan Al-Harami, Turki Al-Ahzam , and Mohammed Al-Sada
Supervisor: Prof. Amr Mohammed
CS Rank 1
Project title: Nusmi3uk: An Arabic sign language system
Students: FatemaElzahraa Elrotel , Hams Gelban, Rouaa Naim, and Sara Said
Supervisor: Dr. Mohammad Saleh
CS Rank 2
Project title: JerboLab: An Educational Standalone Self-Hosted Home Lab for Hands-On Learning and Development
Students: Mohamed Salih, Abdollah Kandrani Abdulla Al-malki, and Sultan Al-Saad
Supervisor: Dr. Moutaz Saleh
CS Rank 3
Project title: FitMate – Your Partner in Prime”.
Students: Shatha Alhazbi , Sharifa Al-Ansari, Shamaim Hamid, and Fatma Almohanadi
Supervisor: Prof. Saeed Salem


