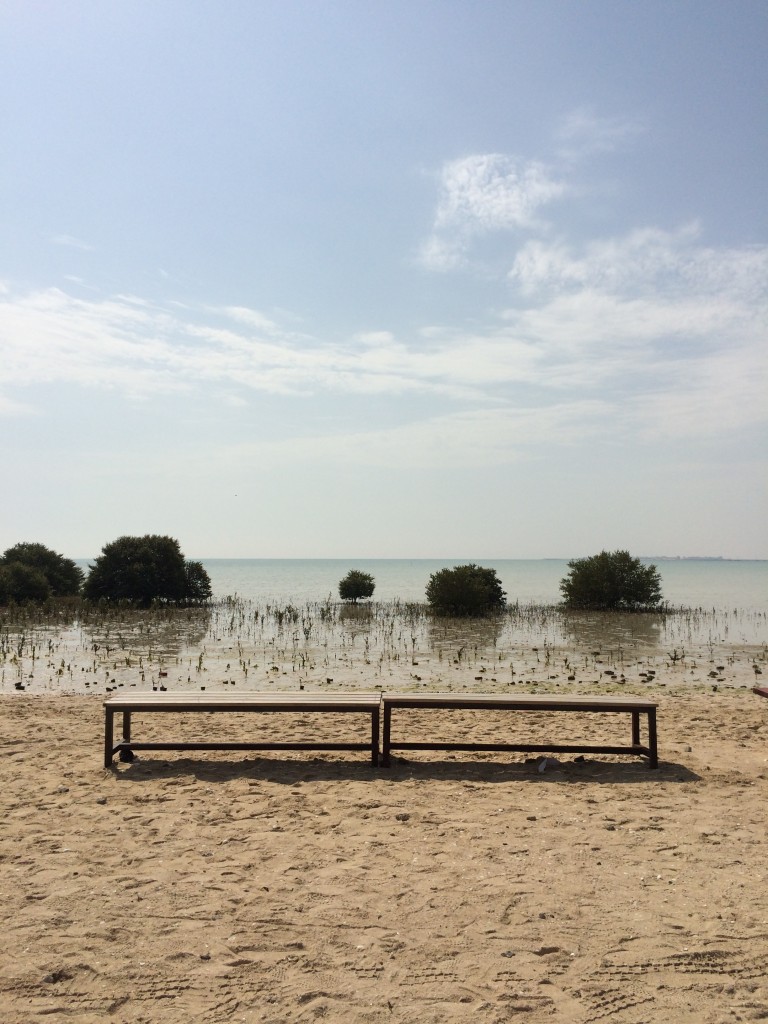
Information from the field trip: Saturday 8 march 2014 soil is unstable and unsuitable for building foundation soil and sand soft nearer to the mangroves and water, and harder towards the heart of the field. The sea water keep pushing the sand dunes The seaside is usually the main element of interest, visitors of different ages usually go first to visit the seaside. Also, during observing the field, people need to get closer to birds and mangroves to explore the field. all the previous reasons mean that visitors will get in contact with the soft sand area close to seaside. Types of soil and sand :
- Sabkha : Sandy sabkha
Sabkhas represent a very distinctive geomorphologic feature in the Qatar peninsula. They cover about 7% of the land surface.Investigations recognized two main types of sabkhas; the first is the Inland Sabkhas which is more mature. The second is the coastal sabkhas or supratidal flats which are more wide spread. Both types are characteristically flat containing a shallow water table, with highly saline ground water. This ground water may be either directly connected with the sea or with continental groundwater. Also surface water from tidal flooding and rainfall and run-off partially recharge the system. Sediments are mainly evaporates, quartz grains and mud, sodium chloride is very frequent on the surface. sabkhas near the inhabited areas and cultivated depressions. Detailed investigation revealed that the origin and evolution of sabkhas in Qatar are greatly influenced by: The low lying topography of the country, the shallow to very shallow coasts, the hot to very hot climate, sea level changes, ground water, geological setting, and anthropological interference. In the subsurface environment of sabkha several minerals are being continously formed as an example (halite, dolomite , calcite) . The crystal growth pressure exerted by the new minerals can be very large . frequant moisture change and presence of excessive . salts in the soil is responsible for many kinds of foundation problems . 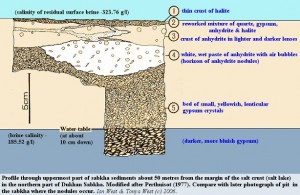 Local Consideration before building in a sabkha soil
Local Consideration before building in a sabkha soil
- using sulphate resisting cement
- the aggregates usedshould be clean (water used should be pure)
- concrete should be dense
- sand grading for concert should be carefully checked
- blinding of sand from different areas or with other materials such as crushed rock fines
- for light structure up to 2 or 3 stories generally shallow foundation are good
- foundation should be painted with hot bitumen to prevent chemical attack from soil and water (tanking)
Some Notes
- Damage to the building can be avoided by designing for a lower bearing pressure or by improving the soil properties
- for heavy foundation loads,piles are adequate
- the Depth of water table and it’s seasonal fluctuation significantly affect the life of foundation concrete in sabkha soil
Sandy beach Qatar peninsula has beaches galore with a 563 kilometre-long sandy coastline. Sandy beaches are soft shores that are formed by deposition of particles that have been carried by water currents from other areas. The transported material is in part derived from the erosion of shores, but the major part is derived from the land and transported by rivers to the sea. The two main types of beach material are quartz (silica) sands of terrestrial origin and carbonate sands of marine origin. The carbonate sand is weathered from mollusk shells and skeletons of other animals. Other material includes heavy minerals, basalt (volcanic origin) and feldspar. Sandy beach is considered as shifting sands located in a region of crashing waves. Each time a wave pummels the shore, sediment is suspended and scattered in every direction. Together the wind and waves constantly rework and reshape the face of the beach. Throughout the year, the beach slope is continually changing. During the spring and summer, gentle constructive waves deposit sediment on the beach platform, building up the slope. The large destructive waves of fall and winter strip the sand from the beach, often leaving only cobblestones and the rocky beach platform. 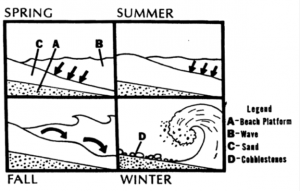 Sandy shores or beaches are loose deposits of sand, gravel or shells that cover the shoreline in many places. It is an extremely dynamic environment where sand, water and air are always in motion. Thus, building construction on these sands is impossible for its instability, continuous motion, and erosion factors.
Sandy shores or beaches are loose deposits of sand, gravel or shells that cover the shoreline in many places. It is an extremely dynamic environment where sand, water and air are always in motion. Thus, building construction on these sands is impossible for its instability, continuous motion, and erosion factors.
Mangroves@Al Khor, Qatar
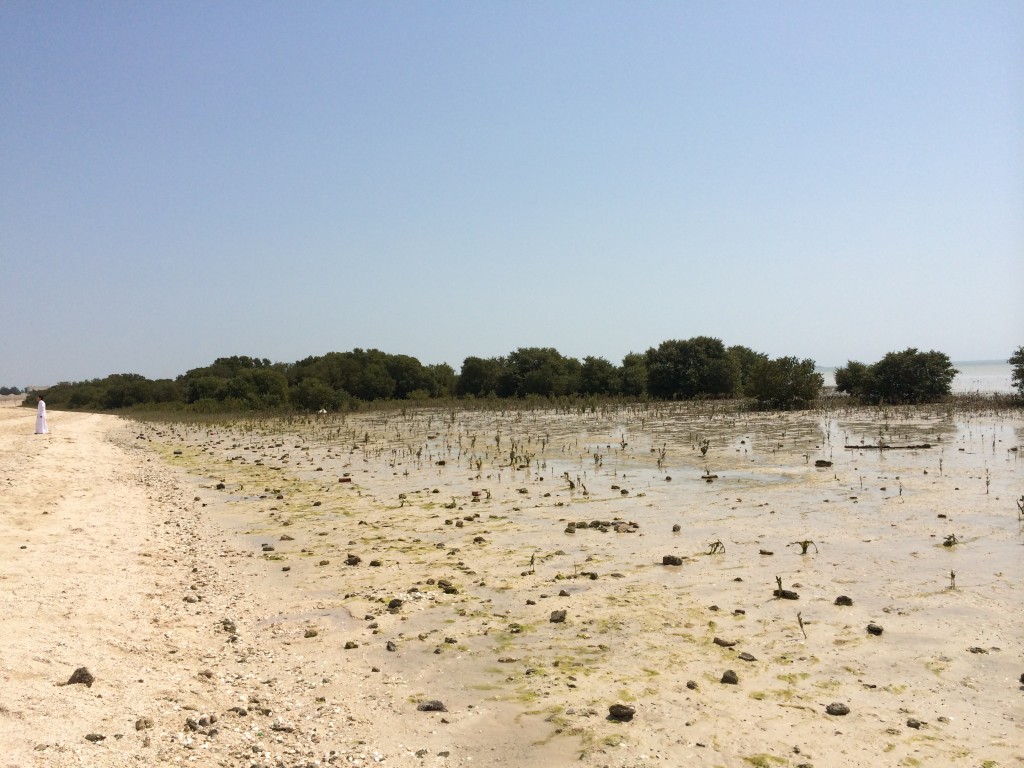 Mangroves (Al-Gurm) are evergreen trees and grow up to a height of 5 meters along the coastal areas of Qatar. Mangrove swamps were a common sight in the Arabian peninsula and were used as building materials and forage for livestock in the past. Along the coast line of Qatar scattered mangrove plantations still can be observed. Avicinnia marina is the predominant mangrove species found in the region.
Mangroves (Al-Gurm) are evergreen trees and grow up to a height of 5 meters along the coastal areas of Qatar. Mangrove swamps were a common sight in the Arabian peninsula and were used as building materials and forage for livestock in the past. Along the coast line of Qatar scattered mangrove plantations still can be observed. Avicinnia marina is the predominant mangrove species found in the region.
*Avicinnia marina Commonly known as grey mangrove or white mangrove. It is distributed along Africa’s east coast, south-west, south and south-east Asia, and Australia.It is one of the few mangroves found in the arid regions of the coastal Arabian Peninsula, mainly in sabkah environments in the United Arab Emirates,Qatar,Oman,as well as in similar environments on both side of the RedSea (in Yemen, SaudiArabia,Egypt,Eritrea,and Sudan),and southern Iran along the Persian Gulf coast.It is also found in the mangroves of South Africa where it is one of the two most dominant mangroves.
Mangrove forests which provide food and shelter for birds, fish, dugongs and rare sea turtles.The Gulf state of Qatar has mangrove forests that are in danger of being damaged or destroyed by developers who want to “eat up the shorelines” according to The Gulf Times.Efforts are now being made to preserve and restore these natural buffers from severe storms; and which also provide havens for birds, fish and other animals.Studies also indicate that mangrove forests may store up to eight times more carbon than tropical rain forests.
Ajmal Khan, Qatar’s Shell Professor in Sustainable Development and Professor at the Department of International Affairs at Qatar University told the paper that mangroves are comprised of species of plants that can withstand the harsh weather conditions in Qatar.He explained that the mangrove’s root systems anchor the plants into the underwater sediment, thereby slowing down incoming tidal waters and allowing organic and inorganic material to settle into the sediment surface.
-resource: -http://www.greenprophet.com/2013/12/qatar-must-stop-shoreline-development-to-save-mangrove-forests/#sthash.1qWw0EsM.dpuf
