Cables Characteristics:
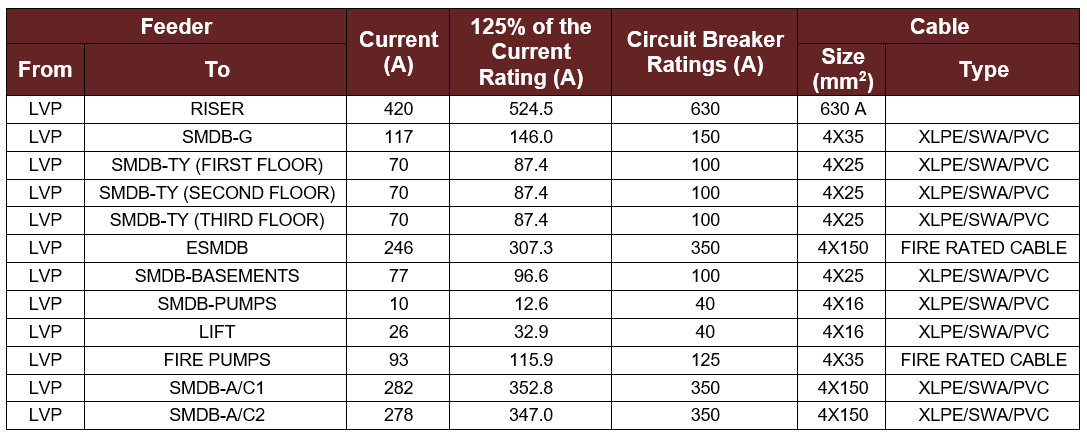
The SMDBs are connected to the LVP by cables that have specific characteristics to be able to handle the current ratings for the total connected load in each SMDB because of that they must be chosen carefully. The size of the cable depends on many factors such as the current rating, the type of the cable, and the location of the cable whether it is underground or in air [5].
The size of the cable is specified by the derating factor and the circuit breaker rating. Simply, these rating factors can be considered in the calculation to determine cable sizes for each SMDB by multiplying the designed current with 125% and the values computed was compared with the circuit breaker ratings or sizes in Qatar and a suitable one was chosen.
It is important to mention that the type of cable used is four cores, since all the SMDBs have three-phase power supply to be able to provide the required current for the load connected to it. Additionally, the cables are chosen to be XLPE insulated, steel wire armoured, and PVC sheathed to handle the harsh weather in Qatar. However, for the fire pump and the emergency submain distribution board the cables are fire rated cables because they should be operating in case of fire. The results obtained for the cables are shown in table 4-2.
Table 4-2: The Cable Size and Type
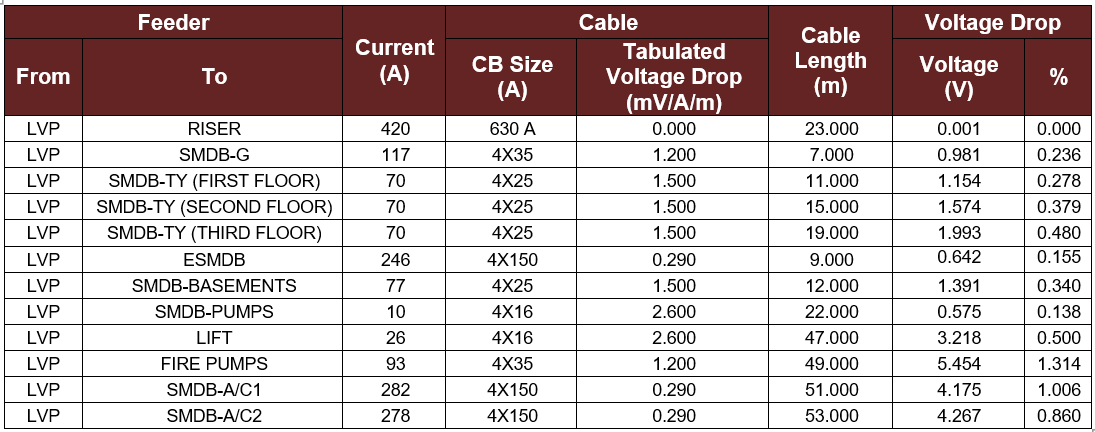
Voltage Drop:
The voltage drop is a significant parameter in designing a distribution substation, so it should be calculated. As per Kahramaa standards the voltage drop can be determined using the following equation (4-7) [5]:

The design current is the current of the total connected load before finding the circuit breaker ratings. Finally, the length is the length of the cables from the LVP to the SMDB which was found from the building outline. The values were obtained as shown in table 4-3.
Table 4-3: The Length of the Cable and the Voltage Drop Calculations