- Characteristics and Types of Circuit Breakers
- Types of Circuit Breakers
- Designing of Circuit Breaker
Characteristics and Types of Circuit Breakers
A circuit breaker is a switching device that interrupts the abnormal or fault current. It is a mechanical device that disturbs the flow of high magnitude fault current and in additions to that, circuit breakers can perform the function of a switch. The circuit breaker is mainly designed for monitoring the level of electrical current and the process closing or opening of an electrical circuit, thus protects the electrical system from damage or any hazards. Circuit breaker essentially consists of fixed and moving contacts. These contacts are touching each other and carrying the current under normal conditions when the circuit is closed. When the circuit breaker is closed, the current carrying contacts, called the electrodes, engaged each other under the pressure of a spring. Many classifications of circuit breakers are made according to the features of that model or the construction type or the application which the breaker will be used in.
Types of Circuit Breakers
- Miniature circuit breaker (MCB): A miniature circuit breaker automatically switches off electrical circuit during an abnormal condition of the circuit. Lately, the MCB is more used in the electrical low voltage applications instead of the fuse, since the miniature circuit breaker is more reliable and safer than the fuse. Whenever continuous overcurrent flows through MCB, the bimetallic strip is heated and deflects by bending. This deflection of bimetallic strip releases a mechanical latch. As this mechanical latch is attached with the operating mechanism, it causes to open the miniature circuit breaker contacts, and the MCB turns off thereby stopping the current to flow in the circuit. To restart the flow of current the MCB must be manually turned on. This mechanism protects from the faults arising due to overcurrent or overload. The typical current ratings for MCB are from 0.5 A to 125 A. Short-circuit ratings may be up to 25 kA which is according to BS EN 60898.
- Moulded case circuit breaker (MCCB): The MCCB uses a temperature sensitive component with a current sensitive electromagnetic component to provide the trip mechanism for protection and isolation purposes. Which enables the moulded case circuit breaker to overload protection, electrical fault protection against short circuit currents, and electrical switch for disconnections. MCCB contains a bimetallic contact which consists of two metals which expand in two different rates when exposed to high temperature. The bimetallic component allows the current to flow during the normal situation, in case of a high current the metal will start to heat and bend away due to the thermal different rates of heat expansion. Which will cause the metals to physically push the trip bar and unlatching the contacts. In addition to the tripping mechanism of the MCCB, it can be also used as manual disconnections switches in case of maintenance operations of emergencies. The Typical current ratings for MCCB are from 16 A to 1600 A though ratings up to 3,200 A are available. Short-circuit ratings may be up to 100 kA. These ratings are according to BS EN 60947-2.
- Air circuit breaker (ACB): Air Circuit breakers generally have two pairs of contacts. The main pair of contacts carries the current at normal load and these contacts are made of copper metal. The second pair is the arcing contact and is made of carbon. When the circuit breaker is being opened, the main contacts open first. ACBs are normally used as the main incoming protection and have a spring-operated mechanism to open and close the device often charged by an internal motor. The protection settings will include time delays and the devices will have a short time withstand value to give full discrimination under fault conditions with downstream protection devices. The typical current ratings for ACBs are 630 to 6,300 A. Short-circuit ratings may be up to 150 kA. Which is according to BS EN 60947-2.
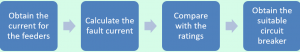
Designing of Circuit Breakers
|
Circuit Breaker Selection |
||||
|
Cable coordination |
CB Specification |
|||
|
TX until LV panel |
Current (A) | Derating Current (A) |
CB type |
|
|
Stadium LV panel |
868.12 | 1,296 |
MCCB |
|
|
Sport activity LV panel |
991.23 | 1,296 |
MCCB |
|
|
LV panel until distribution board |
||||
|
Sport activity LV panel |
AC |
488.65 | 534 |
MCCB |
|
Socket + pump |
248 | 269 |
MCCB |
|
|
Lighting |
458.3 | 475 |
MCCB |
|
|
Firefighting |
270.8 | 296 |
MCCB |
|
|
Stadium LV panel |
AC + change room |
100.35 |
116 |
MCB |
|
Audience + bathroom |
239.25 | 269 |
MCCB |
|
|
Poles (1+2) |
484.54 | 534 |
MCCB |
|
|
Poles (3+4) |
484.54 | 534 |
MCCB |
|
| Parking + street | 379.4 | 384 |
MCCB |
|
| Firefighting | 294.83 | 331 |
MCCB |
|