According to Kahramaa standards, the circuit breakers are controlled by an overcurrent relay. The sizes of the circuit breakers are determined by adding 25% to the total calculated current for the SMDBs and DBs, but for the substation’s devices, the circuit breaker must equal to the current carrying capacity of these devices. Furthermore, the type of circuit breaker depends upon the current, if the current is above 630 A the air circuit breaker (ACB) should be used and if it is less the moulded case circuit breaker will be installed (MCCB).
Dry Type Transformer:
For this project, the rating of the dry type transformer was found to be 1000 kVA and the current carrying capacity is 1334 A. Therefore, the circuit breaker size will be 1600 A controlled by overcurrent relay. The circuit breaker type is three phase air circuit breaker (TP ACB).
Diesel Generator:
The diesel generator rating is 250 kVA. Hence, the circuit breaker size will be calculated as follows:
The generator current is found to be 347.8 A. However, a moulded case circuit breaker (MCCB) with a rating of 350 A was chosen based on the availability in Qatar.
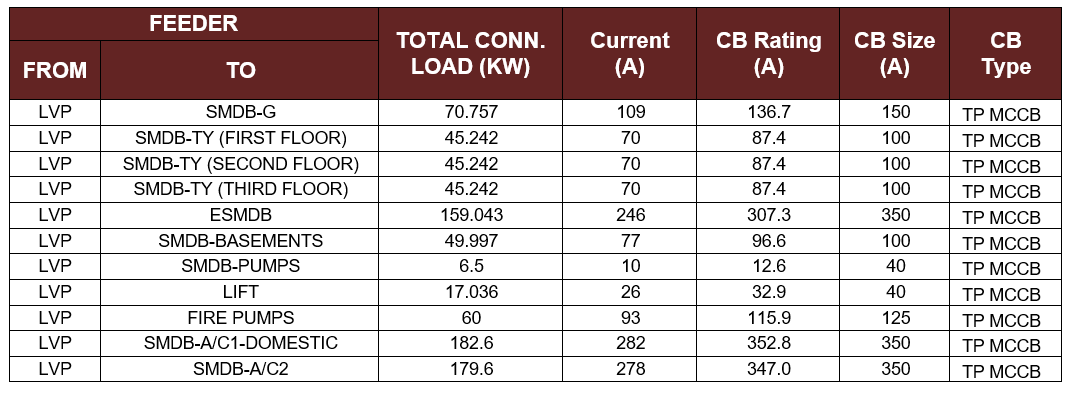
Sub-Main Distribution Boards (SMDBs):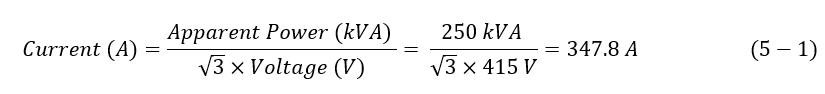
The circuit breaker size and type for the SMDBs are shown in Table 5-1:
Table 5-1: The CB Size and Type for SMDBs
Distribution Boards (DBs):
Each sub-main distribution board is branched to multiple final distribution boards to distribute the electrical power effectively and reliably. According to Kahramaa regulations [5], each distribution board should have an individual circuit breaker to isolate the distribution board from the system in case of a fault. Moreover, for distribution boards which supply socket-outlet circuits, a minimum of 40 A circuit breaker should be installed. The DBs design and CB size and type are illustrated from Table 5-2 to Table 5-5.
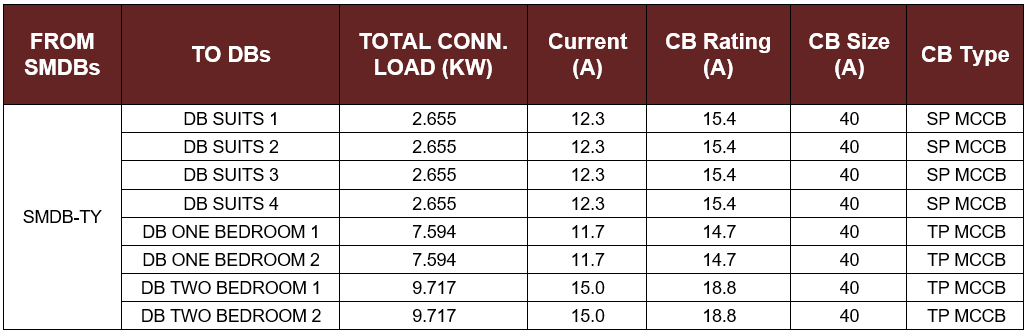
Table 5-2: The CB Size and Type for the DBs of one Residential Floor
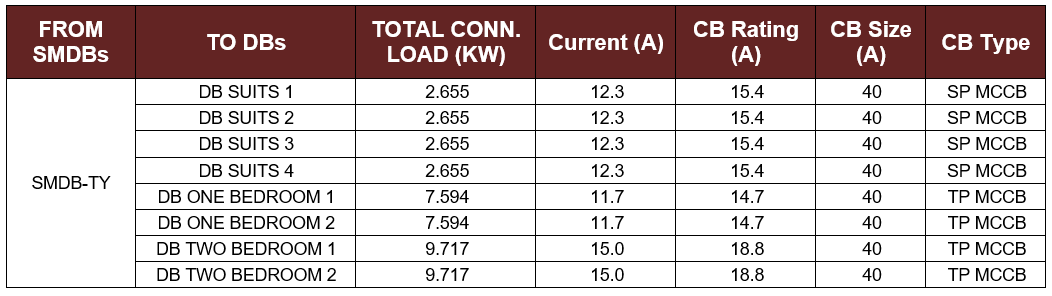
- In this building there are three typical SMDBs for the first three residential floors and they will be branched into eight distribution boards one for each room as shown in Table 5-2 to facilitate the maintenance and isolate the faulted distribution board without affecting other rooms.
Table 5-3: The CB Size and Type for the DBs of Ground Floor
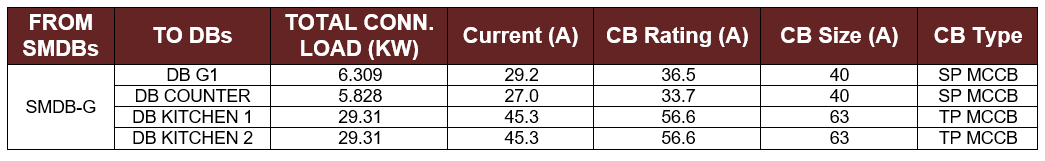
- To meet with the constraints, the panel board of the kitchen was divided into two distribution boards (Table 5-3), as the load of the kitchen will exceed the maximum allowable load of a three phase distribution board which is equal to 60 kW.
Table 5-4: The CB Size and Type for the EDBs of Emergency Submain Distribution Board
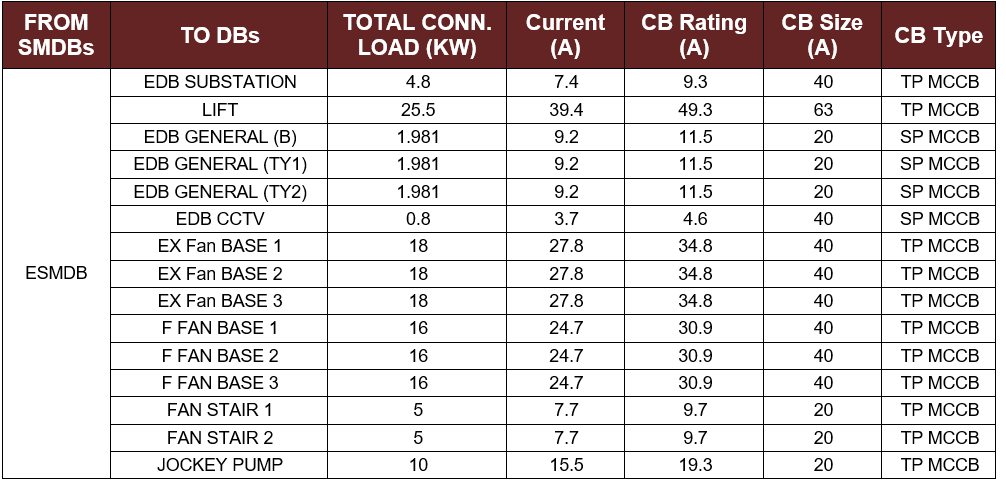
Table 5-5: The CB Size and Type for the DBs of the three Basements
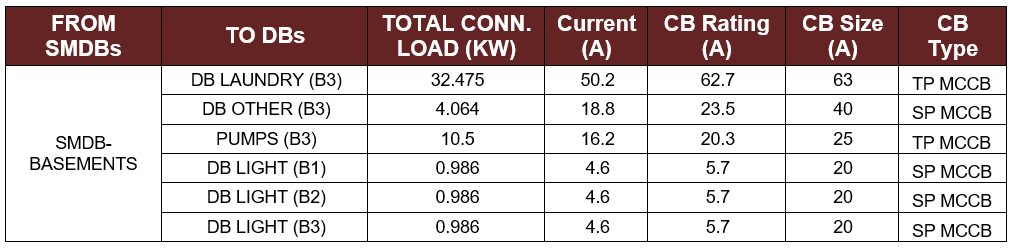
It is important to note that the type of the circuit breaker was selected to be three phase (TP) MCCB. However, for minor connected load the single phase (SP) circuit breaker was utilized. Due to the availability in the market in Qatar, the miniature circuit breaker (MCB) will not be used in this project.
Riser:
There is one riser in the building that delivers and distributes the power to six floors (from the fourth floor to the ninth floor). A circuit breaker will be installed for the whole riser (the details are shown in Table 5-6). Then, six SMDBs will be connected to the riser, which means one for each floor. Additionally, the typical SMDB will be branched to eight DBs to distribute the electricity for the apartments. Nevertheless, each SMDB and DB will have its circuit breaker as demonstrated in Table 5-7 and Table 5-8.
Table 5-6: CB Rating and Type for the Riser
Table 5-7: CB Details for the SMDBs
Table 5-8: CB Size and Type for the DBs