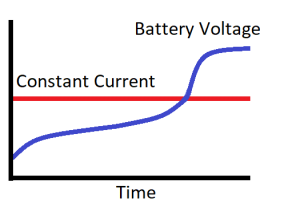
Constant Voltage (CV)
Power is supplied until the voltage of the battery reaches a predefined value. After that, the voltage source supplies enough power to maintain the voltage value at that level.
Constant Current (CC)
Charging by this method is by supplying a constant current to the battery where the voltage across it gradually increases. However, the voltage across the battery does not reach its maximum due to the internal impedance of the source.
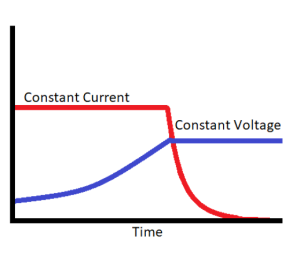
Constant-current Constant-voltage (CCCV)
This method is a combination of both CC and CV. The current is continuously supplied in the first phase until the predefined voltage is reached. Then, the second phase starts when the voltage level is kept constant until the current decays eventually because of the lack of potential difference. For fast charging, large currents are supplied at the first stage.
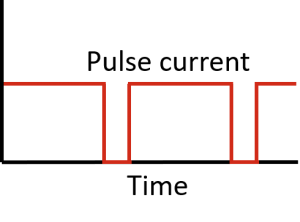
Pulse Charge
This method is by supplying controlled current pulses to the battery while having a relaxation time for the battery to stabilize its chemical reactions. This method requires complex hardware and data manipulation for sensing the voltage, current, and temperature while charging.
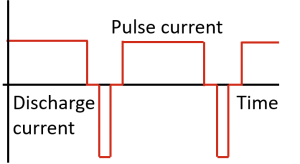
Reflex Charge (also called Negative Pulse Charging or Burp Charging)
In this method, during an off-time, a short discharge pulse is applied. During this discharge pulse, any gas bubbles are dislodged, hence the name “burp” charging. This method prevents damage of the battery.
Go Back to Previous Page
Go Back to FG4 Main Page