EV Charging Methods
Charging EV is done in two ways, which are conduction and induction. For example, conduction charging is done through a cable that is connected between EV and the source. While induction is done wirelessly between transmitter and receiver. Note that it is explained in the next sections. Table 2‑1 below is showing a comparison between conduction and induction charging for EV. [5]
Table 2‑1: Comparison between Conductive and Inductive.
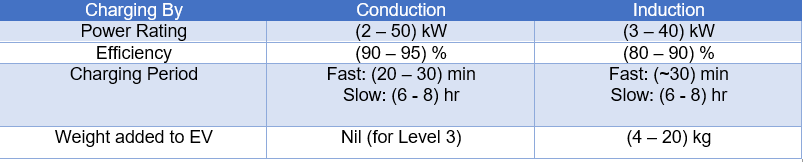
Note that some EVs have both options for charging by (conduction or induction), while other EVs only have one method. Besides, charging by induction is still under development, and the cost is high compared with the conduction method. [6]
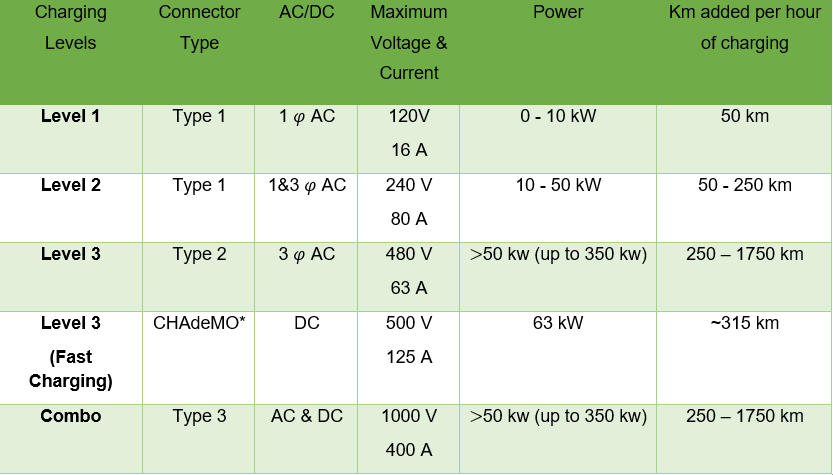
Charging EV by conduction is divided into three levels according to power, connector, and current (AC or DC). Note that there is an assumption related to km per hour of charging (1 kWh = 5 km). Table 2‑2 below is representing different kinds of charging power levels. [7]
Table 2‑2: Comparison between Conductive and Inductive levels.
Charging Stations and Connector Types
Since most of EVs are charged by conduction, it requires multiple kinds of power levels and designs. Besides, power stations are needed in various qualities according to the local and global standards that are used in a particular country. For instance, the standards that are used (IEEE) 519-2014, (IEC) 61000, Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) J2894, and Gobio Recommended Standards (GB/T) 14549.
On the other hand, the connector types are following the same STD. Connectors types are classified into three categories, which are ultra-fast chargers, fast chargers, and conventional chargers. Besides, conventional charging is used in residential places while fast and rapid charging is used in work and public places.
Besides, the connector that is used is distinct from one country to another. For example, in the US, they use (SAE) J1772 for types 1 and 2, (SAE) J3068 is used for AC level 3, and for DC CCS Combo is used. However, China uses one type of connector for all levels, which is (GB/T20234).
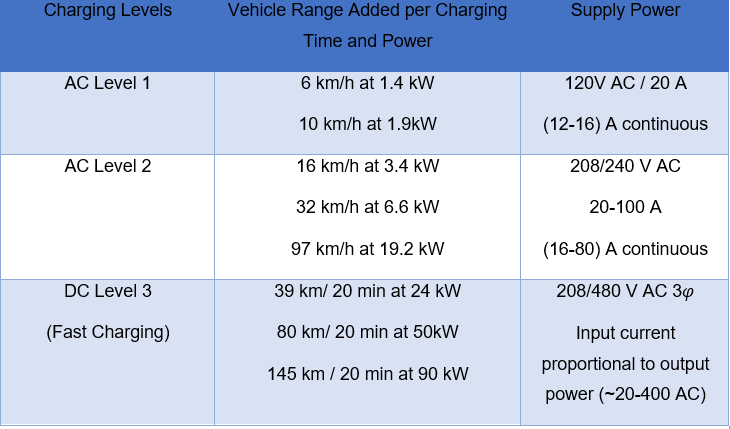
For charging stations, there are three kinds of charging stations. AC level 1, AC Level 2, and DC fast charging. Table 2-3 below is showing different types of charging stations with charging time and amount of power supply. [6]
Table 2‑3: Types of Charging Stations.
On-Board Charging Methods
Since OBC is limited by constraints like space, weight, reliability, efficiency, and high power (fast charging), it requires to study a variety of parameters like charging methods, unidirectional or bidirectional, and integrated and non-integrated circuit. [2]
The important component of OBC is the battery used and the way it will be recharged. Since the Lithium-Ion battery is used, it is important to choose a suitable method of charging. In general, there are various types of charging which are constant voltage, constant current, taper current, pulsed charge, trickle, float charges, and IUI and random charging ways. The most popular way of charging is the constant voltage and constant current charging. A constant voltage is done by step down the voltage to a constant level using a transformer, then rectifier it to DC that will be used to charge the battery. It is a simple and cheap method of charging and using a car’s battery. The type of battery that can be charged by constant voltage is lead-acid and lithium-ion.
Constant current charging method based on varying the level of the voltage to keep the current constant under a certain range. This method is used for specific battery’s cells like nickel-metal hydride and nickel-cadmium cells. the taper current way of charging is dangerous when the battery is overcharged because it is charged a simple and unregulated source of constant voltage. This way of charging is only used for a certain type of battery. The pulsed charge method is a controlling method of current that is fed to the battery in terms of pulses. In this way, the chemical reaction inside the battery cells will be controlled to give maximum efficiency and increasing the battery’s life cycle. Another type of charging is negative pulse charging or (Burp Charing). It is a different way of using current pulses by generating a short pulse of discharge to stabilize the chemical reaction inside the battery. [4]
Charging by constant current-voltage-current (IUI) is a newly developed way of charging that takes two different methods of charging and used them to establish a different charging method. It is started by a constant current rate of charging until the voltage a set point. After setpoint, the charging method is transformed into a constant voltage. Then the constant current is used again to drop the level of the voltage another set point. This method will provide more balancing for battery cells which will improve the life cycle of the battery. Besides, it is considered as a fast way of charging for lead-acid batteries. Trickle charge or continuous charge is designed to compensate for the battery discharging itself. It is using constant current for a long-time charging. This method is not suitable for some types of chargers that have overcharging issues like nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) and lithium batteries. [5]
The float charging method is used for batteries that are connected parallel across the DC source by constant voltage held at a lower level of batteries voltage limit. This method is used for back-up systems as an emergency. a lead-acid battery is used the float charging method. Random charging or self-charging is related to automatic machines that are used to charge the battery while it is active like motors. This way will charge the battery without any control. However, a specific limit of voltage and current should be identified. [8]